Composition and Formation of Black Granite
What Is Black Granite? A Geological Overview
What most people call black granite isn't actually granite at all according to geologists. It falls under categories like gabbro or anorthosite instead. These are types of intrusive igneous rocks created when silica rich magma cools slowly deep down in the earth's crust, somewhere between 25 and 45 kilometers below ground level. The Geological Society of America mentions this whole process takes around 160 million years give or take. During that time, big mineral crystals have plenty of room to grow and form. True granite has a lighter color because it contains more alkali feldspar minerals. But black granite gets its distinctive dark appearance from minerals rich in iron and magnesium such as biotite and hornblende that basically take over where the feldspar would normally be found.
Mineral and Chemical Makeup: Quartz, Feldspar, and Mica
Black granite found in commercial applications actually has much less quartz content compared to regular granite varieties. We're talking about just 5 to 15 percent quartz versus the typical range of 20 to 60 percent in standard granites. The main components here are plagioclase feldspar which makes up around 45 to 70 percent of the stone, along with pyroxenes accounting for approximately 10 to 25 percent. Mica is present but generally stays below 3 percent in most samples. This low mica content means there's not much cleavage happening, which helps explain why these stones tend to be so structurally stable. When it comes to hardness ratings on the Mohs scale, black granite usually falls between 6 and 7. That puts it a bit behind lighter colored granites that typically measure 6.5 to 7.5 on average. Still, this level of hardness makes black granite plenty tough enough for all sorts of building projects despite being just a touch softer than some alternatives.
Petrographic Variations Across Global Sources
| Location | Dominant Minerals | Grain Size | Chromium Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| India (Karnataka) | Labradorite, Hypersthene | Coarse (3-5mm) | 0.02% |
| Brazil (Paraba) | Andesine, Augite | Medium (1-3mm) | 0.12% |
| South Africa | Bytownite, Enstatite | Fine (0.5-1mm) | 0.08% |
These regional differences influence both aesthetic appeal and mechanical performance, allowing architects to select material based on visual and functional requirements.
How Formation Conditions Influence Composition
The speed at which magma cools down ranges from about half a degree to five degrees Celsius every hundred years according to Geoscience Australia, and this has a big impact on what kind of grains and crystals form. When magma cools quickly near those active tectonic areas, it creates really tiny grains sometimes just 0.2 millimeters across. But if the cooling happens slowly within these stable regions called cratons, then we get much larger crystals that can reach sizes around 5 mm. Back in the Paleoproterozoic era, roughly 2.5 to 1.6 billion years back, there were all sorts of pressure changes going on underground. These ancient shifts actually helped create those beautiful layered patterns in stone that people love so much for their decorative slabs today.
Physical and Mechanical Properties of Black Granite
Density, Hardness, and Compressive Strength Metrics
Black granite typically has a density around 2.65 grams per cubic centimeter according to Geology Science from 2023. This makes black granite roughly 10 to 15 percent denser compared to most types of marble, which explains why it doesn't deform easily under pressure. The rock scores between 6 and 7 on the Mohs scale, similar to what we see with hardened steel, so it holds up really well when used for floors where lots of people walk across daily. When it comes to how much weight it can take before breaking, black granite stands at over 200 megapascals of compressive strength. That's actually more than triple what regular concrete can handle. Because of this incredible strength, architects often choose black granite for important structural elements like parts of bridges or the foundations beneath monuments.
Abrasion Resistance, Water Absorption, and Acid Sensitivity
The stone’s practical durability is defined by key performance metrics:
- Abrasion resistance: € 0.5 mm wear depth after 1,000 cycles (ASTM C241)
- Water absorption: < 0.15% by weight, outperforming 90% of natural stones
- Acid sensitivity: Resists most common acids due to low calcite content; vulnerable only to hydrofluoric acid because of trace quartz
Higher plagioclase feldspar concentrations (55–65% in premium grades) enhance chemical resistance, while biotite mica improves fracture toughness.
Performance Under Load and Structural Suitability
Black granite is highly valued by engineers when they need materials that can handle bending forces and maintain their shape. The material has an elastic modulus ranging from around 50 to 70 gigapascals, which means it can bend slightly under stress without actually breaking. This property makes it especially important for buildings designed to resist earthquakes. Laboratory testing indicates that slabs just 3 centimeters thick can hold up to about 300 kilograms per square meter. That kind of strength explains why we see black granite used so often in places like museum steps and heavy duty workshop tables across industries. And interestingly enough, if sealed correctly, these stones survive more than fifty freeze thaw cycles according to European Standard EN 12371. So even in harsh winter conditions where temperatures fluctuate dramatically, black granite remains a reliable choice for construction projects needing lasting durability.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Resistance to Scratches, Heat, UV Radiation, and Stains
Black granite scores around 6 to 7 on the Mohs scale, which means it can stand up pretty well against daily wear and tear from kitchen utensils or foot traffic on floors. According to data from the Geological Survey published last year, this material stays solid even when exposed to temps over 1,200 degrees Celsius something that most engineered stones just cant handle. What makes black granite really special though are those UV resistant minerals mixed in there like biotite and hornblende. These components stop the stone from losing its color no matter how much sunlight beats down on it day after day for years. And once properly sealed, the surface becomes practically impervious to stains, making it a smart choice for busy households where spills happen all the time.
Behavior in Extreme Weather: Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Humidity
With water absorption below 1% (ASTM C97), black granite resists frost damage in regions experiencing 50+ annual freeze-thaw cycles. However, sustained humidity above 85% can accelerate oxidation in iron-rich variants, particularly where sealing is inadequate. Proactive maintenance mitigates this risk.
The Paradox of High Durability vs. Porosity and Sealing Needs
Despite its strength, black granite has microscopic pores (0.2–0.5 µm) that require sealing every 2–3 years indoors and annually outdoors. A 2023 analysis found unsealed granite absorbs oils 40% faster than sealed stone, underscoring the importance of routine care in preserving both hygiene and integrity.
Long-Term Performance in Harsh Climates
| Climate Type | Key Stressors | Black Granite Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Arctic | Freeze-thaw cycles (50+/yr) | <2% water absorption |
| Desert | Thermal shock (70°C swings) | Zero structural failures |
| Tropical Coastal | Salt spray, 90% humidity | No spalling after 15 years |
Data from the 2023 Global Stone Performance Index confirms black granite outperforms alternative materials in extreme environments when maintained properly.
Aesthetic Features and Surface Finishes
Color Range: Jet Black to Dark Gray with Mineral Flecks
Black granite can be anywhere between really dark black and lighter charcoal gray tones, mostly because of those little black specks called biotite mica plus some amphibole minerals. What makes each piece special is the way quartz runs through it like clear streaks, along with those shiny feldspar bits that stand out against the background. When there's lots of biotite present, the stone tends to look consistently dark throughout. But when different minerals mix together in varying amounts, we get those spotted looks so popular in modern kitchens and bathrooms these days.
Visual Texture Influenced by Mineral Inclusions
Grain size and inclusion density define visual texture. Coarse-grained types (3–5 mm) exhibit dramatic interlocking crystals, ideal for statement surfaces. Fine-grained versions (<1 mm) offer subtler, smoother appearances suited to minimalist interiors. Iron oxide deposits may introduce reddish-brown veining, adding warmth to monolithic designs.
Polished, Honed, and Flamed Finishes Explained
| Finish Type | Appearance | Key Features | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polished | Glossy, reflective | Enhances depth; stain-resistant | Countertops, wall panels |
| Honed | Matte, velvety | Minimizes glare; hides minor wear | Flooring, outdoor seating |
| Flamed | Textured, non-slip | Improves traction; weather-resistant | Pool decks, exterior stairs |
As noted in material engineering studies, finish choice affects both light interaction and functional safety. Polished surfaces reflect 70–85% of ambient light, brightening interiors, while honed finishes diffuse illumination evenly.
Matching Finish to Design Style and Functional Needs
Flamed finishes suit rustic or industrial aesthetics but need annual resealing in freeze-prone areas. Polished slabs elevate luxury kitchens but require daily cleaning to manage fingerprints. Industry data shows honed granite reduces slip-fall incidents by 40% in commercial settings compared to polished alternatives, reinforcing its suitability for high-traffic floors.
Applications and Maintenance of Black Granite
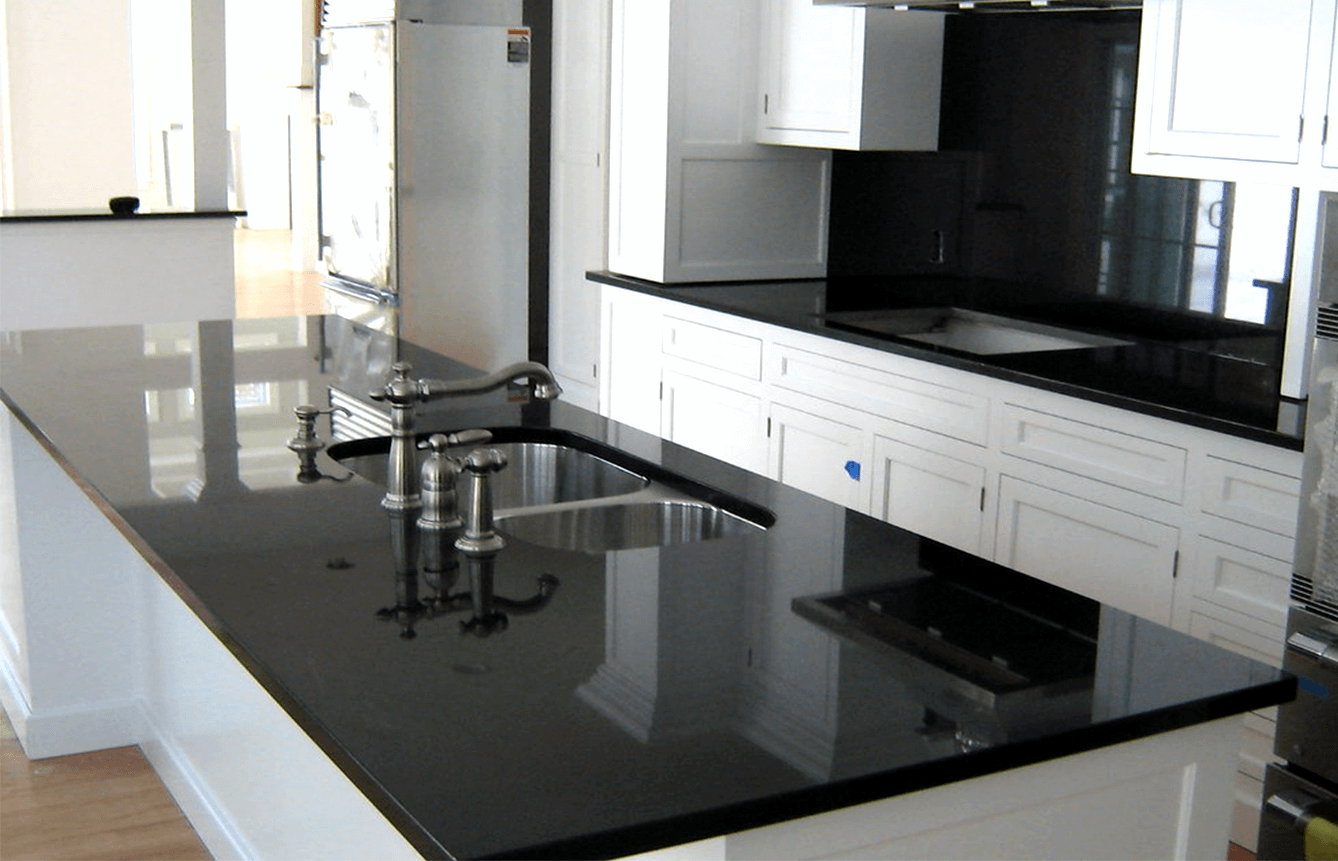
Common Uses: Countertops, Flooring, Cladding, and Monuments
Architects love using black granite because it combines real strength with beautiful looks. According to the latest market data from 2024, around two thirds of all natural stone used in building projects ends up in places like kitchen counters, bathroom floors, and exterior walls. Why? Because these surfaces need materials that won't get scratched easily and don't soak up moisture. The rock's impressive crushing strength somewhere between 200 and 250 MPa makes it great for supporting heavy foot traffic areas. Plus, nobody can deny how striking it looks on the outside of buildings when properly finished. Stone carvers especially appreciate this material for creating lasting memorials since the details in the engravings stay sharp and clear even after many decades of weather exposure.
Interior vs. Exterior Applications and Performance
Indoors, black granite excels as kitchen countertops and bathroom vanities. Outdoors, its thermal expansion coefficient (8–12 µm/m°C) necessitates expansion joints in cladding systems exposed to temperature extremes. In humid coastal zones, it degrades 30% slower than limestone, though quarterly sealing is recommended to prevent salt buildup in pores.
Cleaning Protocols and Sealing Frequency for Longevity
- Daily Care: Use pH-neutral cleaners to preserve sealant integrity
- Stain Management: Blot oil spills within 20 minutes using microfiber cloths
- Sealing Intervals: Every 18–24 months indoors; every 12–18 months outdoors (assess via water droplet test)
Debunking the Myth: Is Black Granite Truly Low-Maintenance?
Despite marketing claims, untreated black granite absorbs liquids at 0.4% by weight, sufficient to harbor bacteria in food-prep areas. Regular maintenance reduces microbial growth by 83% (Indoor Air Quality Institute 2023), proving that longevity depends not just on inherent durability but consistent care.
FAQs About Black Granite
What is black granite and how is it formed?
Black granite, often referred to as gabbro or anorthosite by geologists, is an igneous rock formed when silica-rich magma cools slowly deep within the earth's crust over millions of years.
What are the main minerals found in black granite?
Black granite typically contains plagioclase feldspar, pyroxenes, and sometimes minimal mica, giving it its distinct dark color. It has a lower quartz content compared to typical granite.
How durable is black granite?
Black granite is incredibly durable, scoring 6 to 7 on the Mohs scale. It boasts high compressive strength, abrasion resistance, low water absorption, and is generally acid-resistant.
What are common uses of black granite?
Black granite is extensively used for countertops, flooring, cladding, monuments, and structural applications due to its strength and aesthetic appeal.
How often should black granite be sealed?
For optimal performance and longevity, black granite should be sealed every 18–24 months indoors and every 12–18 months outdoors, with regular assessments using a water droplet test.